Hydroponic Basics
What is Hydroponics?
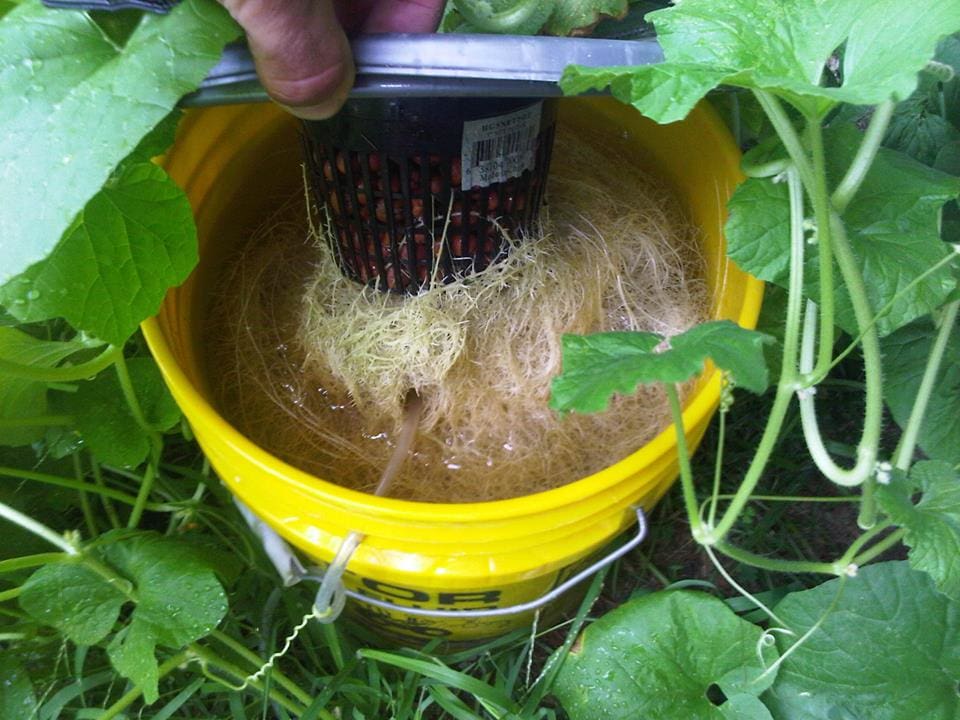

Hydroponics is the method of growing plants in a solution of water and nutrients with or without inert growing media such as sand, coco, perlite, and hydroton. These media are used for supporting the plant and to keep the nutrient solution close to the roots. Hydroponic nutrient solutions are typically aerated because the roots need oxygen for respiration and growth.
What is Aeroponics?
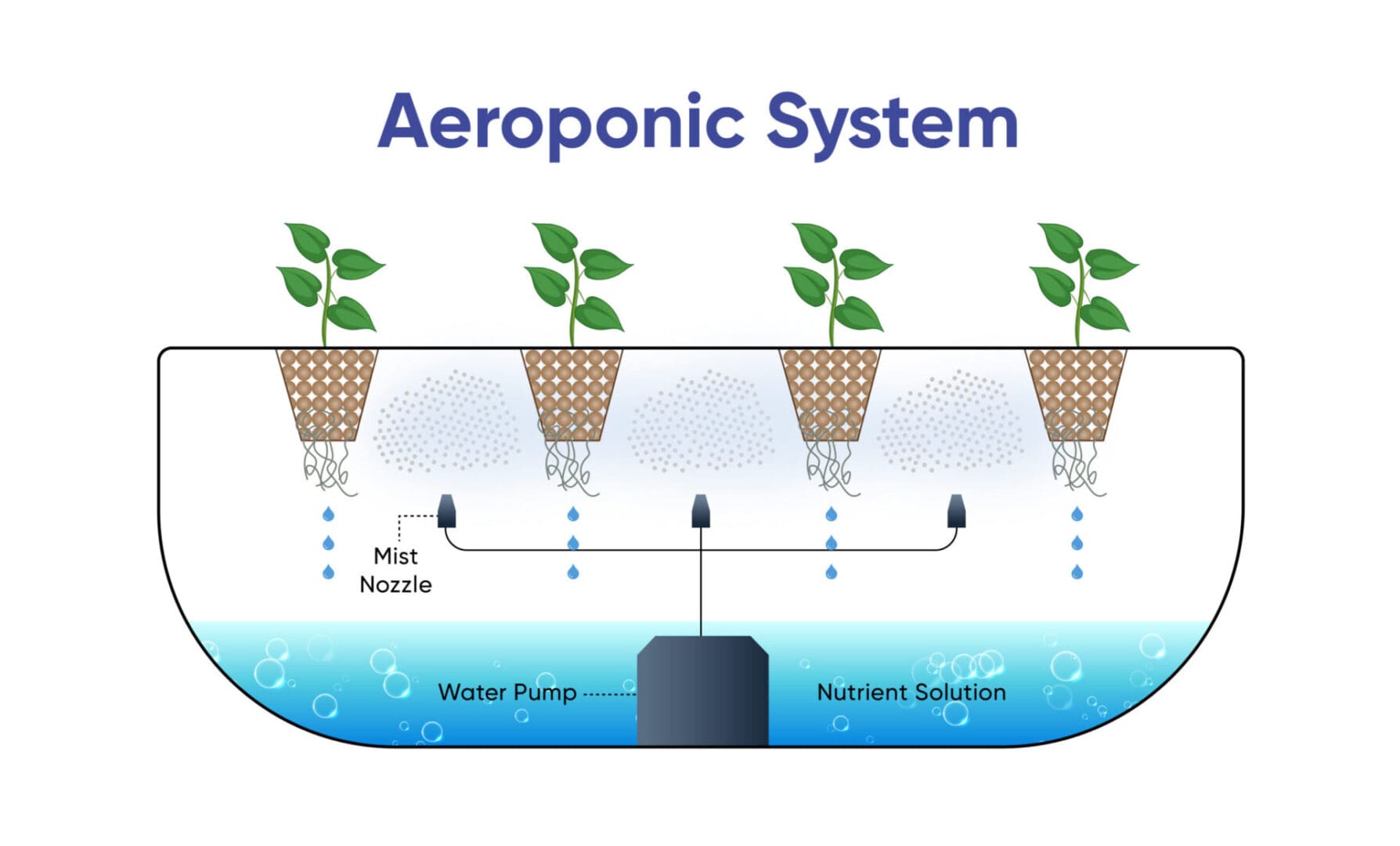
A plant-cultivation technique in which the roots hang suspended in the air while nutrient solution is delivered to them in the form of a fine mist. Aeroponic systems utilize misters and sprayers that periodically spray the roots with aerated nutrient solution. This type of system is a little more difficult to operate but the rapid rates at which plants grow results in amazing yields.
Advantages
- The biggest advantage with hydroponics is the increased growth rates so you get maximum yields in the shortest amount of time. With a properly set up system, your plants will mature faster and provide over 30% increased yields. Properly set up systems include maintaining control of light levels, pH, nutrient solution strength, levels of dissolved oxygen in water, ventilation, and pest control.
- Plants grown hydroponically always have an unlimited supply of water and nutrients which allows the plants to focus most of their energy growing shoots, foliage, fruits, and flowers.
- Plants can be grown hydroponically both indoors and outdoors
- Any plant can be grown hydroponically!
If you are not growing hydroponically, don't worry, Blue Planet Nutrients works excellent in soil as well!
Water Quality
Water is the foundation of all hydroponic systems. It is very important to know the quality of the water being used because most water already contains various minerals which can effect the pH stability of your nutrient solution as well as the availability of the nutrients for absorption by plants.
How Important is Water Quality in Growing?

Water containing excessive calcium and magnesium (ie. "Hard-Water") can cause serious problems. If the dissolved salts in your water supply measure 200 ppm or more, we strongly recommend that you obtain a water analysis to determine calcium content. Excessive calcium is the main factor in determining if your water is hard. If an analysis of your water supply reveals that the calcium content of your water supply is greater than 70 ppm (mg/liter) you should consider purchasing a reverse osmosis water filtration system to filter your water.
Is Chlorinated Water a Problem?
The most common issue regarding tap water and hydroponics is chlorine. Many growers don't realize that chlorine is a micro-nutrient required by plants in extremely minimal quantities. Chlorine is highly volatile and will evaporate from tap water within a day or sooner if the water is aerated. Because plants are able to absorb it, they wind up taking in far too much from unfiltered tap water resulting in diminished growth due to poor root health. The micro-flora and micro-fauna living in the root zone are very important for healthy vigorous plants and high yields. Don't let chlorine kill the good guys!
Chloramines are chemical compounds of ammonia and chlorine that are also used as municipal water supply sanitizers. Chloramines do not evaporate from water the way chlorine does and many water filters which remove chlorine cannot remove chloramine. The effects of chloramine on your garden are even more detrimental than chlorine. If you are concerned your tap water may contain chloramines, have it tested. To avoid problems caused by these chemicals, consider an investment in a water filter or reverse osmosis machine and make sure it takes out both chlorine and chloramine. The improvement in plant health can be considerable which translates to a substantial increase in harvest quality and quantity.
Oxygen and Roots?
Plant root systems need oxygen for aerobic respiration, an essential plant process which releases energy for root growth and the uptake of nutrients. In a deep water culture hydroponic system, it is absolutely crucial to have adequate oxygen levels because roots are submerged. For optimal growth it is recommended to have 1 liter per minute of air pumped into each gallon of nutrient solution. Therefore a 100 gallon reservoir would require a 100 LPM air pump for maximum oxygenation. In every other hydroponic application it is only required to oxygenate the solution enough to prevent it from becoming anaerobic, which means much less air is required. Generally if you have good movement in the solution and the majority of the surface of the solution is broken with bubbles, your plants will do fine. This can be achieved with a simple fish tank pump and air stones.
What About Water Temperature?
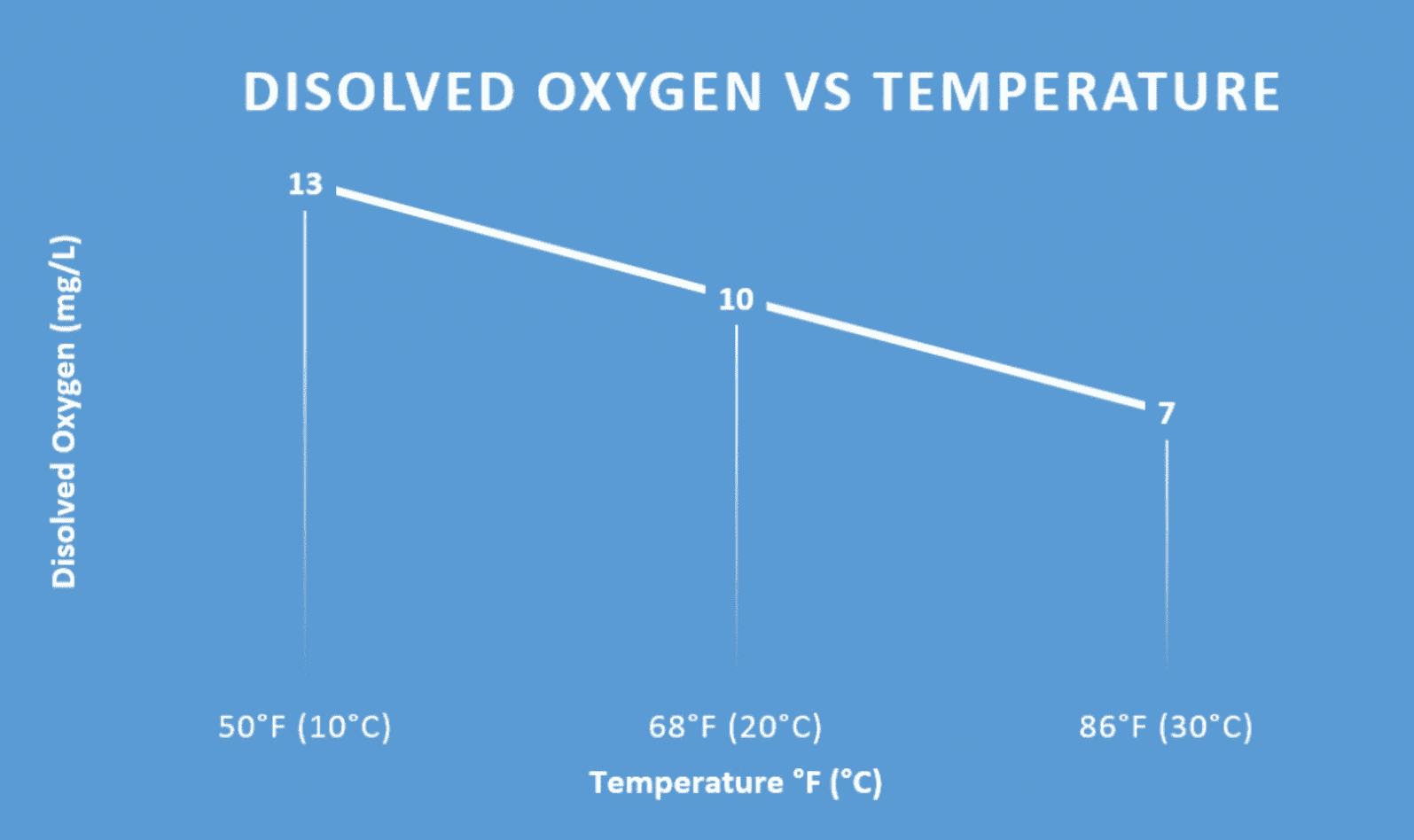
As the temperature of your nutrient solution increases, the less your nutrient solution holds dissolved oxygen. The oxygen content of a fully aerated solution at 10°C (50° F) is about 13 ppm, but once the solution warms up to 20° C (68° F) the oxygen content drops to 9 – 10 ppm. By the time the solution has reached 30° C (86° F), then oxygen content levels are only at 7 ppm. We recommended not exceeding 76° F in your nutrient solution (ideal temp is 24° C or 70° F) in order to keep oxygen dissolved and available for plant roots.
6 Types of Hydroponic Systems
Deep Water Culture
This is the simplest hydroponic system there is. It is the easiest to use and produces wonderful results. In a DWC system, you use a reservoir to hold a nutrient solution. The roots of your plants are suspended in that solution so they get a constant supply of water, oxygen, and nutrients. Air stones and an air pump are used to oxygenate the nutrient solution allowing the roots to respire and grow.
What You Need to Build a Water Culture System:
- Container to hold the nutrient solution (reservoir)
- Aquarium air pump
- Air line/hose
- Air stones (or soaker hose) to create the small bubbles
- Baskets, pots, or cups to hold the plants
- Some type of growing media
How a hydroponic Water Culture system operates is easy. The plant is actually suspended in baskets right above the nutrient solution in the reservoir. Usually by cutting through the lid covering the reservoir. The roots hang down from baskets the plants are in, and hang down directly into the nutrient solution where they are submerged. The roots remain submerged all the time 24/7. The roots don't suffocate because they get the air and oxygen they need from air bubbles rising through the nutrient solution, as well as from dissolved oxygen in the water itself.
The more air bubbles the better for water culture systems. The bubbles rising should make the water look like water boiling at a heavy rolling boil. The bubbles should be rising up through, and making direct contact with the roots as they rise to the top of the water to be most effective for the plants.
Flood and Drain (Ebb and Flow)
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) systems are very popular with home hydroponic growers for many reasons. Besides how easy they are for anyone to build, you can use almost any materials you have laying around to build them with, so you don't need to spend much money to grow plants hydroponically. Also they can be built to fit in any available space you might have (both indoors or outdoors), and there is no limit to the different and imaginative ways to design them for that space. Along with being inexpensive and easy to build, plants grow very well in flood and drain systems. The flood and drain system works basically like it sounds, by simply flooding the plants root system with nutrient solution. Only periodically rather than continuously.
How a hydroponic flood and drain system operates quite simple. The main part of the flood and drain system holds the containers the plants are growing in. It can be just one plant, or many plants/containers in series. A timer turns on the pump, and water (nutrient solution) is pumped through tubing from the reservoir up into the main part of the system using a submersible fountain/pond pump. The nutrient solution continues to fill (flood) the system until it reaches the height of the preset overflow tube so that it soaks the plants roots. The overflow tube should be set to about 2 inches below the top of the growing media.
When the water filling/flooding the system reaches the overflow tube height, it drains back down to the reservoir where it recirculates back through the system again. The overflow tube sets the water level height in the flood and drain system, as well as makes sure the water (nutrient solution) doesn't spill out the top of the system while the pump is on. When the pump shuts off, the water siphons back down into the reservoir through the pump (draining the system).
What You Need to Build a Flood and Drain (Ebb and Flow) System:
- A container for the plant's roots to grow in.
- A container (reservoir) to hold the nutrient solution.
- A submersible fountain/pond pump.
- A light timer to turn the pump on and off.
- Some tubing to run from the pump in the reservoir to the system to be flooded.
- An overflow tube set to the height you want the water level.
Growing medium of some kind.
Drip Systems
Drip systems are one of the most widely used types of hydroponic systems around the world, both for home growers as well as commercial growers alike. That's mainly because it's an easy concept and needs few parts, but yet it's a very versatile and effective type of hydroponic system. Even though it's an easy concept, it won't limit your imagination when building your own systems. The way a drip system works is just like it sounds, you simply drip nutrient solution on the plants roots to keep them moist.
Hydroponic drip systems can easily be designed in many ways, as well as from small to large systems. But their especially useful for larger plants that take a lot of root space. That's because you don't need large volumes of water to flood the system, and the drip lines are easy to run over longer spaces. As well as when using a larger amount of growing media for larger plants, more growing media retains more moisture than smaller amounts, and that's particularly beneficial to large plants because it's more forgiving to the plants. Forgiving meaning that the plants arent as sencitive to watering times, so they don't stress imeditaly if they don't get waterd on time for one reason or another.
What You'll Need to Build a Drip System is:
- A container for the plant's roots to grow in.
- A container (reservoir) to hold the nutrient solution.
- A submersible fountain/pond pump.
- A light timer to turn the pump on and off.
- Some tubing to run from the pump in the reservoir to the plants (and/or the drip lines if you use different sizes).
- Tubing (PVC or flexible tubing) to run the return lines for the extra nutrient solution from the plants back to the to the reservoir.
- (optional) You can use drip emitters, or you can just poke small holes in the tubing with a hot paper clip for the nutrient solution to drip out of like we like to do.
- Growing media for the plants roots to grow in and help support the plants weight.
Nutrient Film Technique
The N.F.T. system is quite popular with home hydroponic growers as well. Mainly because of it's fairly simple design. However N.F.T. systems are best suited for, and most commonly used for growing smaller quick growing plants like different types of lettuce. Along with growing lettuce, some commercial growers also grow different types of herbs and baby greens using N.F.T. systems.
While there are a lot of different ways design an N.F.T. system, they all have the same characteristic of a very shallow nutrient solution cascading downward through the tubing. Where the bare roots of the plants come in contact with the water, and can absorb the nutrients from it. The major downside to an N.F.T. systems is that the plants are very sensitive to interruptions in the flow of water from power outages (or whatever reason). The plants will begin to wilt very quickly any time the water stops flowing through the system.
What You Need to Build a N.F.T. System:
- Container to hold the nutrient solution (a reservoir)
- Submersible fountain/pond pump
- Tubing to distribute water from the pump to the N.F.T. growing tubes
- Growing tubes for the plants to grow in (also called a gully/channel)
- starter cubes, or small baskets and growing media to start seedlings in
- Return system (tubing, channels) to guide the used nutrient solution back to the reservoir
How a hydroponic N.F.T. system operates is fairly simple. Nutrient solution is pumped up from the reservoir, usually to a manifold that connects the larger tubing to a number of smaller ones. Each one of these smaller tubes runs nutrient solution to one side of each one of the growing channels/gully's with the plants in it. A thin layer (film) of the nutrient solution flows through each of the channel's with the plants in it to the other side, passing by each plant and wetting the roots on the bottom of the channel as it does. The nutrient solution flows from one side to the other because the channel is sloped slightly so the water flows down hill.
The plants in the growing tubes (channel/gully) are typically suspended above the water by placing seedlings started in starter cubes or small one inch baskets of growing media into small holes in the top of the tube. The roots of the seedlings hang down to the bottom of the tube/channel where they get nutrients from the shallow film of nutrient solution flowing by. The excess nutrient solution flowing out of the low end of each of the channels drains into another channel or tube, and guided back to the reservoir where it is recirculated through the system again.
Wick System
The wick system is the simplest of all six types of hydroponic systems. That's because traditionally it doesn't have any moving parts, thus it doesn't use any pumps or electricity. However some people still like using an optional air pump in the reservoir. Because it doesn't need electricity to work, it's also quite useful in places where electricity can't be used, or is unreliable.
The wick system is an easy type of system to build when first learning about hydroponics, and/or you just your want to get your feet wet first. This type of hydroponic system is also often used by teachers in classrooms as experiments for kids. Both to help explain how plants grow, as well as getting them interested in hydroponics.
What You Need to Build a Wick System:
- A bucket or container for the plant.
- A bucket or container for the reservoir.
- A good wicking growing media like coco coir, Vermiculite, or perlite.
- Some strips of material like felt or good wicking rope.
How a wick system operates is like it sounds, it basically just wicks up nutrient solution from the reservoir to the plants using the process of capillary action. Meaning it sucks up water to the plants through the wick like a sponge. Typically good wick systems will have at least two or more good size wicks to supply enough water (nutrient solution) to the plant. The bucket/container with the plant in it basically sits right above the container used for the reservoir. That way the water doesn't need to travel up very far to get to the growing media with plants.
Aeroponics
While the concept of the aeroponic system is quite simple, it's actually the most technical of all 6 types of hydroponic systems. However it's still fairly easy to build your own basic aeroponic system, and a lot of home growers like growing in them as well, and even get really good results using this type of hydroponic system.
Like with any other type of hydroponic system, you can use many different kinds of materials to build it, as well as many different types of design setups to fit in your space. Your really only limited by the space you have, and your imagination.
Some advantages to using an aeroponic systems are they typically use little to no growing media. The roots get maximum oxygen, and the plants grow more rapidly as a result. Aeroponic systems also generally use less water than any other type of hydroponic system (especially true aeroponic systems). Also harvesting is usually easier, especially for root crops.
However there are a few downsides to aeroponic systems as well. Besides being a bit more expensive to build. The mister/sprinkler heads can clog from build up of the dissolved mineral elements in the nutrient solution. So make sure to have extras on hand to swap out when they do clog while you clean them. Also because the plants roots are hanging in mid air by design in aeroponic systems, the plants roots are much more vulnerable to drying out if there is any interruption in the watering cycle. Therefor, even any temporary power outage (for any reason) could cause your plants to die much more quickly than any other type of hydroponic system. Also there's a reduced margin for error with the nutrient levels in aeroponic systems, especially the true high pressure systems.
What You'll Need to Build Your Own Basic Aeroponic System:
- Container to hold the nutrient solution (a reservoir).
- Submersible fountain/pond pump.
- Tubing to distribute water from the reservoir pump to the mister heads in the growing chamber.
- Enclosed growing chamber for the root zone.
- Mister/sprinkler heads.
- Water tight container for the growing chamber where the plants root systems will be.
- Tubing to return the excess nutrient solution back to the reservoir.
- Timer (preferably a cycle timer) to turn on and off the pump.
How the aeroponic system operates is a fairly easy concept. First the purpose of the roots hang in mid air is so they can get the maximum amount of oxygen that they can get. The high volume of oxygen the roots get allows the plans to grow faster than they would otherwise, and the main benefit to this type of hydroponic system.
Second, there is typically very little if any growing media is used, exposing all the plants roots. The plants are suspended either by small baskets, or closed cell foam plugs that compress around the plants stem. These baskets or foam plugs fit in small holes at the top of the growing chamber. The roots hang down inside the growing chamber where they get sprayed with nutrient solution from mister heads at regular short cycles. The regular watering cycles keep the roots moist and from drying out, as well as provides the nutrients the plants need to grow.
The growing chamber the roots are in should be light proof, and almost air tight. It does need to allow fresh air in so the roots can get plenty of oxygen, but you don't want water to spill out, or pests to get in. Also you want the root chamber to hold in humidity. Ultimately what you want is the roots to get plenty of moisture, fresh oxygen, and nutrients. A a well designed aeroponics system provides a good balance of all three of those elements to the roots at the same time.
Lastly, a major factor in aeroponic systems is the water droplet size. Roots sprayed with a fine mist will grow much faster, bushier, and with more surface area to absorb nutrients and oxygen with than roots sprayed with small streams of water like from small sprinkler heads. That translates into the plant canopy growing more rapidly as well. Aeroponic system types are categorized by the water droplet size. e Nutrients
Hydroponic Growing Media
Expanded Clay Pellets (Hydroton)
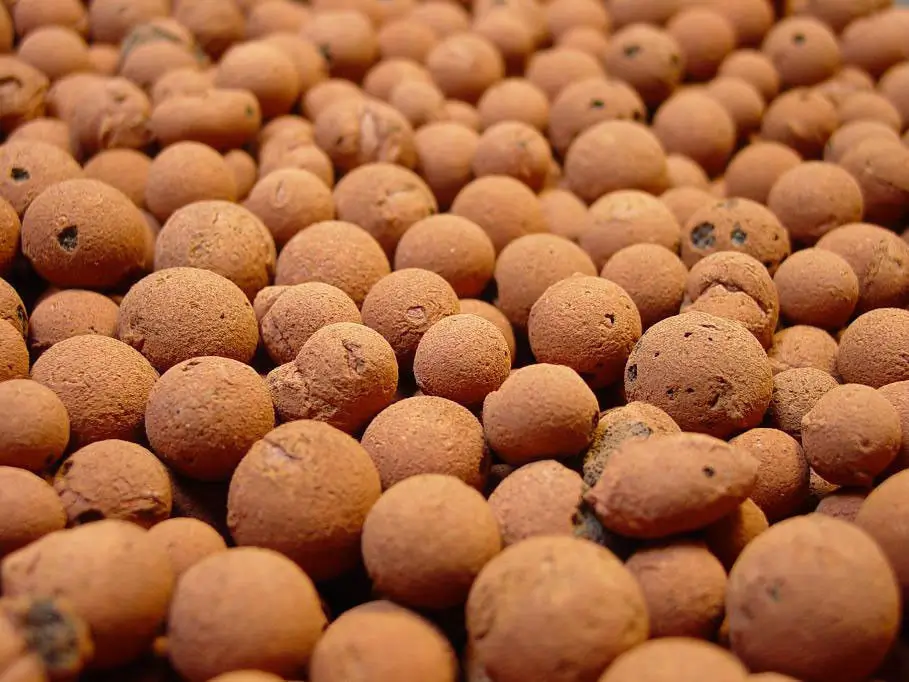

This is a popular growing media because it is so versatile. Expanded clay pellets, or hydroton are about the size of marbles. They are very lightweight making transplanting and harvesting very easy. They are absolutely fantastic for a variety of hydroponic techniques such as DWC, Ebb and Flow, and NFT and are a favorite of small producers using media bed or Dutch bucket techniques. These clay pellets are made by heating clay to over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit using a rotary kiln, which gives it that signature pebbly form. Hydroton has a lot of pore space which allows the nutrient solution to flow through, ensuring roots have access to plenty of oxygen for healthy root growth. It also provides good colonization for microbial populations. Hydroton grow media is reusable, it can be cleaned, sterilized, then reused again.
Coco Coir
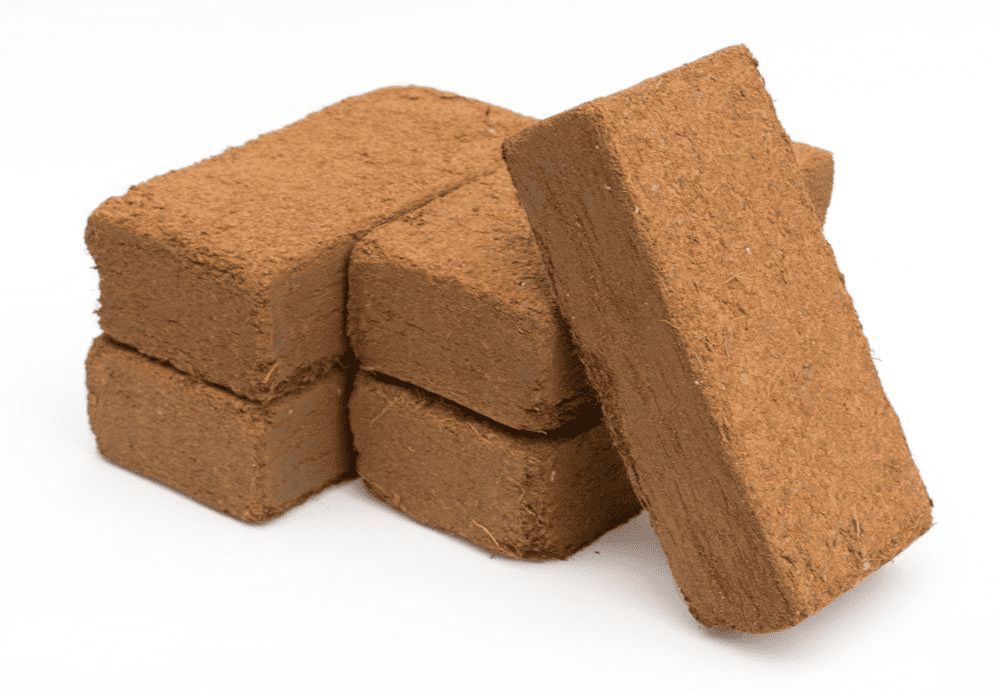

Coco coir is a fantastic all-around growing media. Coco coir (Coconut fiber) is from the outer husk of coconuts. What was once considered a waste product, is one of the best growing mediums available. Coco coir is quickly becoming a favorite among hydroponic gardeners. It has outstanding water and air holding capacity. It can hold eight to nine times its own weight in water and still hold on to around 22% air. Coco coir is an organic plant material, it breaks down and decomposes very slowly, so it won't provide any nutrients to the plants growing in it, making it perfect for hydroponics. Because of its air and water holding capacity and pH, it is a very forgiving substrate and great for beginners. Its anti-fungal properties helps rid plants of soil borne diseases (inhibits pathogens like phythium and phytophthora). The biggest downside with coco coir is build up of salts so it's a good idea to flush from time to time. Good quality, hydroponic grade coco coir will have not have a high salt content, but you should always flush it with water before use until no more tannins are seen (tannins stain or color the water brown).
Perlite
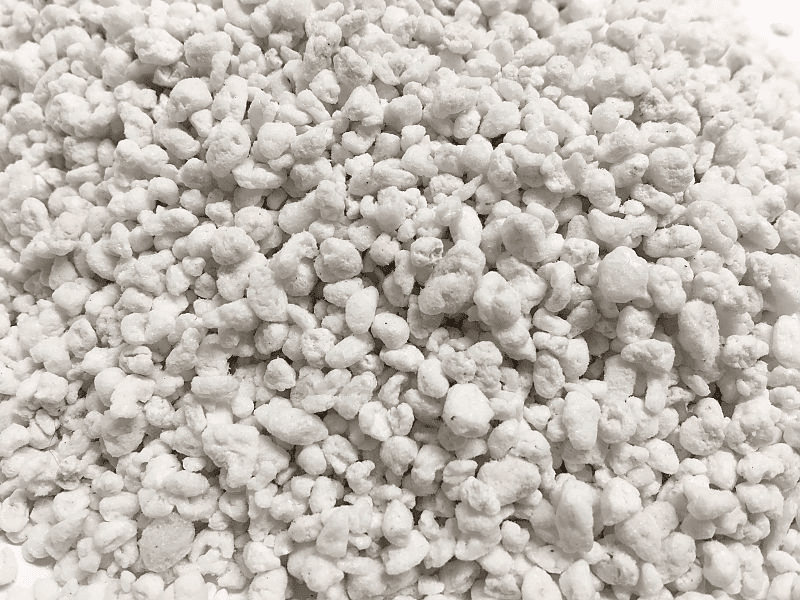

Perlite is one of the best hydroponic growing mediums around. Perlite is something that many traditional soil gardeners already recognize. It’s a soil-free growing medium that has helped to add aeration to soil mixes for years. Perlite is a mined material, a form of volcanic glass that when rapidly heated to more than 1600 deg F to create an extremely light and porous material. It has one of the best oxygen retention levels of all growing media because of how porous it is. Because of the super heated manufacturing process, Perlite is also sterile when you purchase it. It is also pH neutral. Its weight can be a downside in certain hydroponic systems where water interacts directly with the growing media, causing it to shift around and wash away. Because of this, perlite is rarely ever used alone – typically it is mixed with coco coir, soil, or vermiculite.
Vermiculite

Vermiculite very similar to Perlite. It’s a mineral that is heated until it expands into pebbles. It has a high cation exchange capacity and retains more water than perlite and can wick (draw) water and nutrients upwards. The major drawback of vermiculite is that it retains too much water to be used by itself. Vermiculite is most frequently used in conjunction with perlite as the two complement each other well. Vermiculite retains moisture (about 200% - 300% by weight), and perlite doesn't so you can balance your growing medium so that it retains water and nutrients well but still supplies the roots with plenty of oxygen. A 50/50 mix of vermiculite and perlite is a very popular medium for drip type hydroponic systems as well as ebb and flow systems. Vermiculite is commonly used in combination with other types of media to create a highly customized media for specific hydroponic applications. Because of its high water holding capacity, vermiculite is great for Wick systems.
Sand

Sand is the oldest hydroponic media being first used by the Aztecs in the 12th century. Sand is readily available and inexpensive making it one of the most efficient and cost-effective methods of soilless culture. Sand is perhaps the best hydroponic media for drip and drain to waste systems. In drain-to-waste systems, the nutrient solution is not recycled greatly reduces the likelihood of diseases such as Fusarium and Verticillium spreading in the medium. It also means there is no nutrient imbalance since plants are fed with fresh nutrient solution at each irrigation cycle. Sand is commonly mixed with Vermiculite, Perlite, and or coco coir. All help retain moisture as well as help aerate the mix for the roots.
When using sand as a growing media you will want to use the largest grain size you can get. That will help increase aeration to the roots by increasing the size of the air pockets between the grains of sand. Mixing Vermiculite, Perlite, and or coco coir with the sand will also help aerate. You will also want to rinse the sand well before use to get as much of the dust particles out of it as you can. One big downside to using sand as a growing media for hydroponics is that it is very heavy. 3-4 gallons of wet sand can weigh up to 50lbs. So you won't want to be moving it once you get it set up. Or use it in a ratio of something like 20%-30% sand and the rest Vermiculite, Perlite, or another type of growing media to reduce weight.
Rockwool

Rockwool is one of the most common growing media's used in hydroponics and is the most widely used substrate for the commercial production of hydroponic tomatoes. It is made by melting rock and spinning it into extremely thin and long fibers, similar to fiberglass. They take these fibers and press them into cubes of varying sizes. Rockwool is a sterile, porous, non degradable medium. Rockwool comes with a high pH should be pH balanced before use. That's done by soaking it in pH balanced water before use. Rockwool has all of the benefits of most growing media, with some pretty serious downsides. The fibers and dust created in the spinning and compressing process can be harmful to eyes, nose and lungs. You can prevent the dust by immediately soaking rockwool in water once you take it out of the package.
Essential Plant Nutrients
Plants require 16 essential elements for growth: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), sulfur (S), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), and chlorine (Cl).
These 16 essential elements, also called nutrients, are often split into two groups. Plants obtain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) from air and water. Growers do not need to provide these nutrients, so they are not sold as fertilizers. The other 13 essential are provided by fertilizers.
Macro Nutrients
Macro nutrients are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are required by plants in the greatest amounts compared to the rest. These are the nutrients that are displayed on the front of fertilizer products such as 13-13-13... 13%N 13%P 13%K
Nitrogen
- It is absorbed by plants in two major ionic forms: Nitrate (NO3–) and ammonium (NH4+)
- Nitrogen is a part of all living cells and is a necessary part of all proteins, enzymes and metabolic processes involved in the synthesis and transfer of energy
- The most recognized role of nitrogen in the plant is its presence in the structure of protein molecule
- Nitrogen is a part of chlorophyll, the green pigment of the plant that is responsible for photosynthesis
- Essential for plant cell division, vital for plant growth
- Aids in production and use of carbohydrates
- Affects energy reactions in the plant
Phosphorus
- Phosphorus is absorbed primarily as the monovalent inorganic phosphate anions (H2PO4–)
- Involved in photosynthesis, respiration, energy storage and transfer, cell division, and enlargement Promotes early root formation and growth
- Major constituent of the energy transfer molecule ATP
- Involved in the formation of oils, sugars, and starches
- Helps early root growth and helps to establish seedlings quickly
- Increases water-use efficiency
- Encourages Blooming and Fruit Growth
Potassium
- Regulation of water in plant cells
- More than 60 enzymes require K for their activation
- Plays an important role in photosynthesis and translocation of photosynthates
- Helps in the formation of proteins and chlorophyll
- Carbohydrate metabolism and the break down and translocation of starches
- Increases water-use efficiency
- Essential to protein synthesis
- Increases disease resistance
Secondary Nutrients
The secondary nutrients are calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. For most crops, these three are needed in lesser amounts that the primary nutrients.
Calcium
- Absorbed is absorbed as divalent Ca2+
- Essential part of cell walls and required for the formation of new cells
- Utilized for Continuous cell division and formation
- Involved in nitrogen metabolism
- Reduces plant respiration
- Aids translocation of photosynthesis from leaves to fruiting organs
- Increases fruit set
- Stimulates microbial activity
Magnesium
- Phosphorus is absorbed primarily as the monovalent inorganic phosphate anions (H2PO4–)
- Involved in photosynthesis, respiration, energy storage and transfer, cell division, and enlargement Promotes early root formation and growth
- Magnesium is absorbed as divalent Mg2 +
- Key element of chlorophyll production. 15-20% of Mg remains in chlorophyll
- Improves utilization and mobility of phosphorus
- Activator and component of many plant enzymes
- Increases iron utilization in plants
- Influences earliness and uniformity of maturity
Sulfur
- Sulphur is taken up by the plants from the soil as divalent sulphate anions (SO42-)
- Essential for production of protein
- Promotes activity and development of enzymes and vitamins
- Helps in chlorophyll formation
- Improves root growth and seed production
- Helps with vigorous plant growth and resistance to cold
- Aids in seed production
- Necessary in chlorophyll formation (though it isn’t one of the constituents)
Micro Nutrients
The micronutrients are boron, chlorine, cooper, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc. These elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients.
Iron
- Plants take up Fe as the ferrous (Fe2+) cation
- Iron is a component of many enzymes associated with energy transfer, nitrogen reduction and fixation, and lignin formation
- Important part of enzymes and aids in protein synthesis, photosynthesis and the metabolic functions of plants Promotes formation of chlorophyll
- Acts as an oxygen carrier
- Reactions involving cell division and growth
Manganese
- Manganese functions primarily as part of enzyme systems in plants
- It activates several important metabolic reactions and plays a direct role in photosynthesis
- Manganese accelerates germination and maturity while increasing the availability of phosphorus (P) and calcium (Ca)
- Helps photosynthesis and the metabolic functions of plants
- Manganese helps in chlorophyll formation
Zinc
- Zinc (Zn) is taken up by plants as the divalent Zn+2cation
- High yields are impossible without it
- Aids plant growth hormones and enzyme system
- Zinc influences the formation of some growth hormones in the plant
- It is involved in auxin metabolism
- Necessary for chlorophyll production
- Necessary for carbohydrate formation
- Necessary for starch formation
- Aids in seed formation
Copper
- Copper (Cu) activates enzymes and catalyzes reactions in several plant-growth processes
- The presence of copper is closely linked to Vitamin A production, and it helps ensure successful protein synthesis
- Acts as a catalyst in photosynthesis and respiration
- It is a constituent of several enzyme systems involved in building and converting amino acids to proteins.
- Important in carbohydrate and protein metabolism and formation of lining in plant cell walls.
- Affects the flavor, the storage ability, and the sugar content of fruits
- It helps in the utilization of iron during chlorophyll synthesis
- Increases sugar content
- Intensifies color
- Improves flavor of fruits and vegetables
Boron
- Boron (B) exists taken up by plants as the BO33- anion
- B supports the structural and functional integrity of plant cell membranes
- Assists in the metabolic function of plant and aids in cell division
- Increases the mobility of calcium in the plant
- Acts as a regulator of K/Ca ratio in the plant
- Required for the development of new cells in meristematic tissue
- Necessary for proper pollination and fruit or seed setting
- Essential for seed and cell wall formation
- Promotes maturity
- Necessary for sugar translocation
Molybdenum
- Essential component of the major enzyme nitrate reductase in plants
- A structural component of nitrogenase, the enzyme actively involved in nitrogen fixation by root-nodule
bacteria of leguminous crops, by some algae and by free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria - Reported to have an essential role in iron absorption and translocation in plants
- Aids in the formation of legume nodules
- Needed to convert inorganic phosphates to organic forms in the plant
Chlorine
- Plants take up chlorine (Cl) as the chloride (Cl-) anion
- Active in energy reactions in the plant
- Not much information about its functions
- Can interfere with P uptake
- Enhances maturity of small grains on some soils
pH Adjustment
What is pH?
pH is the measure of acidity/alkalinity of an aqueous solution. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline. Pure water has a pH very close to 7
What pH is Best for Growing Plants Hydroponically?
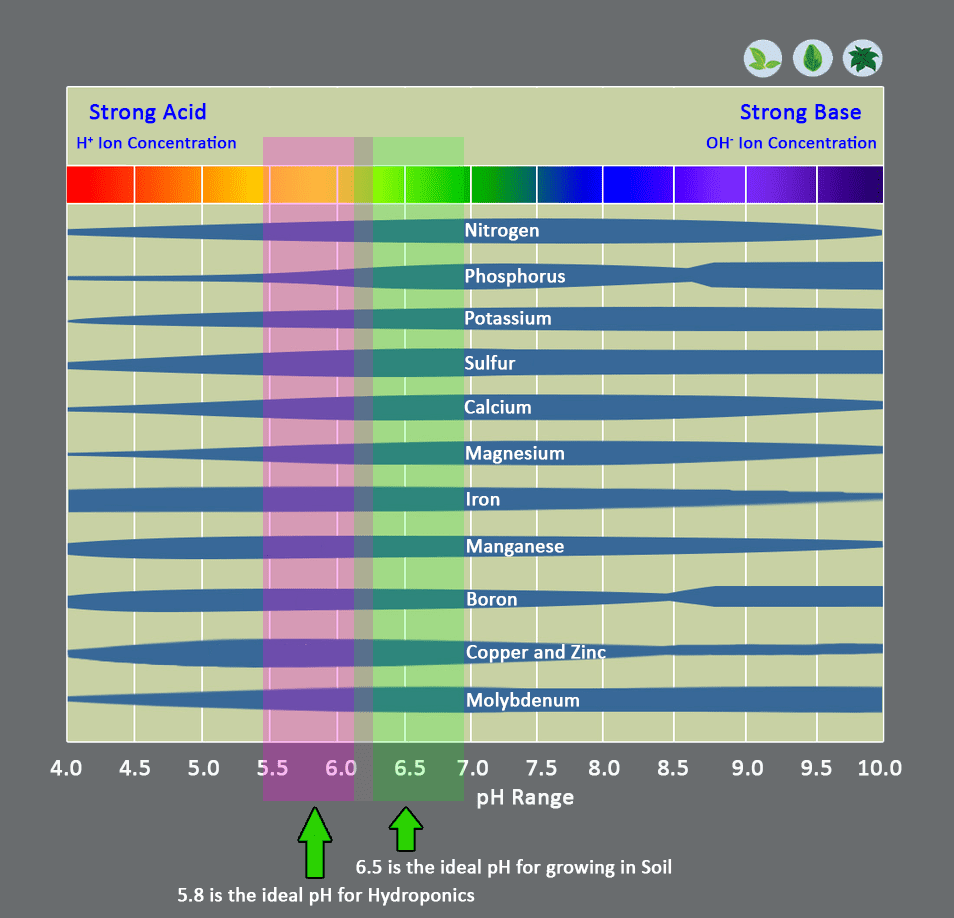
The ideal pH range for most hydroponic crops is between 5.5 and 6.3 with 5.8 being the standard pH value for most crops.
What pH is Best for Growing Plants in Soil?
The ideal pH range for most soil grown crops is between 6.0 and 7.0 with 6.5 being the standard pH value for most crops grown in soil.
How Does pH Level Affect Plant Growth?
pH is important because it affects availability and absorption of the nutrients required for plant growth. In hydroponic culture, maximum absorption of these nutrients is typically at a pH of 5.8. In soil culture, maximum absorption of essential nutrients is typicallly at a pH of 6.5. When pH falls below this range many of the macro elements (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, and S) have less availability and Macronutrient deficiencies will develop. When pH values rise above this range, many micronutrients (Fe, Mn, B, Cu, Zn) become unavailable for plant uptake and micronutrient deficiencies will develop.
How Are pH Levels Managed in Hydroponic Nutrient Solutions?
pH is adjusted by using an acid to lower it or a base to raise it. Blue Planet Nutrients pH Down and pH Up are designed for this purpose. Many acids and bases are extremely corrosive and dangerous, so care should be used if you are not using a product labeled for hydroponic use.
How Are pH Levels Managed in Soil?
pH can be measured in soil by measuring the leachate as it drains out of the bottom of a pot after watering or feeding a plant. The best way to adjust the pH of a soil solution is to adjust the pH of the nutrient solution up or down before feeding to the plant. The leachate (liquid draining from the bottom of containers) should consistently have a pH of 6.5. Adjust the nutrient solution that you are feeding to plants grown in soil by using an acid to lower it or a base to raise it. Blue Planet Nutrients pH Down and pH Up are designed for this purpose.
How Often Should I Check My pH Level?
When first starting out it's a good idea to measure the pH of your water every day until you get a feel for your system. Measure your water and then add your nutrients. Within an hour check the pH and adjust accordingly. Repeat this process until pH stabilizes. Both the Elite Series 3-Part and the Blue Max 2-Part contain special pH buffers to help maintain a desirable pH. It is a good idea to note how much water, nutrients and pH modifiers are needed to obtain the desired values. After several "start- ups" you can generally get a feel for how much acid or base to use for your situation. Frequently, pH stays within a desirable range for a considerable time, and then rapidly rises or falls to an extreme. This is usually an indication of the need to do a nutrient change. If you are using hard water, pH has the tendency to climb above 7.5. If you are using hard water with a starting ppm value of greater than 200 PPM, it is advisable to purchase a Reverse Osmosis water filtration system to produce pure water.
How Much pH Up/down is Needed Per Gallon?
Blue Planet Nutrients pH UP and Down is very concentrated. Start out by adding just a drop or 2 per gallon. Stir and wait about 5 or 10 minutes, and test your water again. Frequently you will only need 1 to 2 ml of pH Up/Down per gallon of water. You may need additional pH Up/Down if you have hard water. Blue Planet Nutrients 3-part and 2-part base nutrients are pH buffered to facilitate keeping the pH in a favorable range.
The pH in My System Drops Below 4 Every Few Days After Cleaning and Refilling. How Do I Increase the pH and Stabilize It?
The easiest way is to continue adding pH Up. This is generally fine because the additional elements that are added are potassium ions. Potassium is frequently the highest element in hydroponic nutrient solutions. Sometimes pH crashes because of the presence of a large amount of microbial activity in the nutrient solution. This is usually a result of poor maintenance of the system due to infrequent nutrient changes or other stresses. The best way to avoid this scenario is to keep a clean system with adequate nutrition. Other times, rapidly growing plants can rapidly change the ionic ratio of various nutrients causing an imbalance causing large fluctuations in pH. For instance, if a plant is favoring nitrate over ammonium ions, then the pH of the nutrient solution could drop rapidly. The best fix for this is to continue to add pH UP or to dump your reservoir and add fresh nutrients.
TDS, EC and PPM
What Does a TDS or EC Meter Measure?
TDS and EC meters are used to measure nutrient solution strength. Nutrient ions have an electrical charge. Electrical Conductivity "EC" is a measurement of all those charges in the solution that conduct electricity. The greater the quantity of nutrient ions in a solution, the more electricity that will be conducted by that solution. Electrical Conductivity (EC) is expressed in siemens per centimeter (s/cm) or milliseimens per centimeter(ms/cm).
What Does the Term Parts Per Million (PPM) Mean?
Total dissolved solids (TDS) is typically expressed in parts per million (PPM). PPM is a common unit for measuring the concentration of elements in nutrient solutions. One ppm is one part by weight of the mineral in one million parts of solution. Example: A solution of nutrients dissolved in water at a strength of 500 ppm means that there are 500 milligrams of dissolved solids present for every liter of water.
How Do I Convert Between TDS (PPM) and EC Readings?
Multiply the EC reading (in milliSiemens/cm) by 1000 and divide by 2.
To get an EC value, multiply the ppm reading by 2 and divide by 1000.
For example, if your EC is 1:
1*1000/2= 500 ppm.
And if your ppm is 500:
500*2/1000= 1 EC
All TDS and EC meters measure electrical conductivity and then convert the EC measurement to PPM using a conversion factor. There are three conversion factors which various manufacturers use for displaying ppm's:
USA 1 ms/cm EC 1.0 = 500 ppm
European 1 ms/cm EC 1.0 = 640 ppm
Australian 1 ms/cm EC 1.0 = 700 ppm
For Example:
Hanna, Milwaukee1 ms/cm EC 1.0 = 500 ppm
Eutech1 ms/cm EC 1.0 = 640 ppm
Truncheon1 ms/cm EC 1.0 = 700 ppm
Why is Measuring and Monitoring Nutrient Solution Strength Important?
Delicate plants, cuttings, and seedlings can experience fertilizer burn if the nutrient solution strength is too high. Once the plants begin growing and have developed a healthy root system, the strength of the nutrient solution can be increased. Some plants prefer a milder nutrient strength, while others grow better and produce better quality fruit with a higher concentration. The stronger your nutrient solution is, then more food is available to your plants. 1500 PPM is the maximum nutrient solution strength that most plants can handle before showing signs of fertilizer burn.
How Often Should I Calibrate My TDS or EC Meter?
Before each use or at least once a week. Use standard reference solutions and follow the calibration instructions that came with your meter.
However, be careful of very high levels as this can burn and or kill the plant.
Interactive 500 Scale EC/PPM Conversion Chart
The Great Debate: Organic Vs. Mineral Fertilization
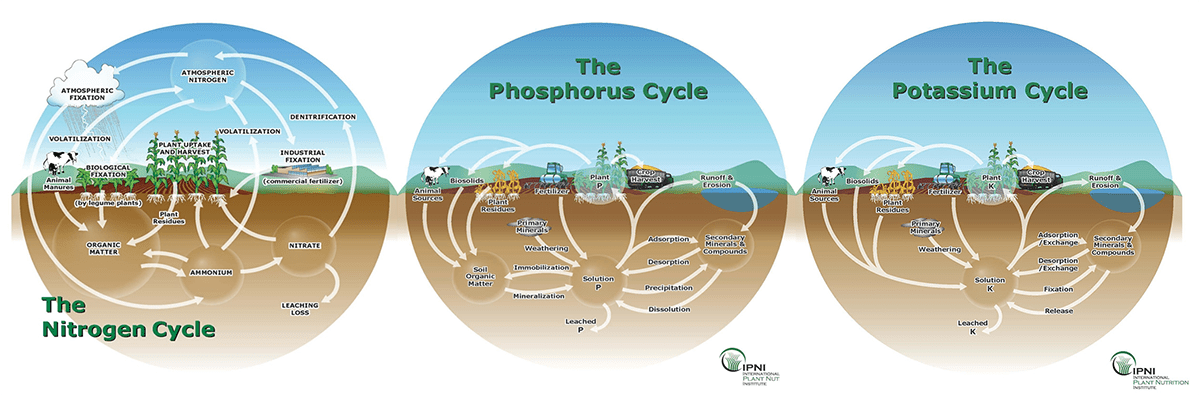
Growing "organically" involves fertilizing plants with only organic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are derived from organic sources, more specifically, it must contain carbon. The nutrients in organic fertilizers must be broken down by microorganisms in order for them to be usable by plants.
Mineral based fertilizers on the other hand, are immediately available for plants to use for growth.
The only difference in the nutrients in organic fertilizers vs. mineral based fertilizers are the nutrients in organic fertilizers once part of living tissue.
An example that I like to use often when educating folks on this topic is using compost (organic) as a source of nitrogen fertilizer vs. using ammonium nitrate (mineral salt).
Ammonium nitrate is immediately for use by plants because it is already in a form that plants can use: ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-). The compost provides the plant with both ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) but these ions are incorporated into organic matter which must be broken down by microorganisms to release them before they can be used by plants.
There is no difference at all in the NH4+ and NO3- in inorganic salts and the NH4+ and NO3- that once was part of the compost. In fact, the nitrogen that is in the compost was at one point nitrogen gas in the atmosphere. All nitrogen that has ever been incorporated into living organisms was nitrogen gas in the atmosphere that was fixed into ammonia (NH3) through a natural process called "nutrient cycling". Certain plants such as legumes can fix nitrogen directly from the air. Ammonium nitrate is made using the "Haber Process" which uses energy to take nitrogen out of the air and turn it into a salt that can be used as fertilizer. This salt is very pure and only consists of NH4+ and NO3- that is immediately available for plant uptake.
In conclusion, nitrogen is nitrogen regardless if it was part of decomposed compost or a mineral salt. In fact, all nitrogen that is part of all living organisms was once gas in the atmosphere and vice versa. Plants just need it to be in 2 forms to be used NH4+ and NO3-. Nutrient cycling is responsible for this. ALL plant nutrients are part of a nutrient cycling process regardless if the nutrients are liquid in a bottle or decomposing organic matter. All elements in organic matter could have at one time been considered "inorganic".
